Redundancy Concepts in Profinet
CTE is constantly working to increase the availability of our customers' systems. Ethernet-based communication systems are therefore primarily used for high-availability systems. These offer several advantages: Not only can system availability be made more dynamic with different redundancy options, but the systems are also faster.
In automation systems, fieldbuses are an essential element for the communication of various components with a control system. Due to the ever-increasing demands on their availability and speed, serial fieldbuses such as Profibus are increasingly reaching their limits. For this reason, they are gradually being replaced by Industrial Ethernet-based systems. These provide greater flexibility in the connection and offer an increased transfer speed of up to 1 Gbit per second. This flexibility means that the system can be equipped with different redundancy options depending on the availability requirements.
The three most important for Industrial Ethernet systems are controller redundancy, network redundancy and logical redundancy within the software. There are many options on the market for solutions with Industrial Ethernet. One that has established itself in the European market is Profinet. Profibus & Profinet International Group (PI) launched Profinet back in 2003 as an alternative to Profibus. Initially, however, this new format was slow to gain acceptance. In recent years, the technical advantages of Ethernet-based solutions and the growing portfolio of supported hardware have made Profinet one of the market leaders in Europe. In addition, Profinet offers many advantages in terms of availability.
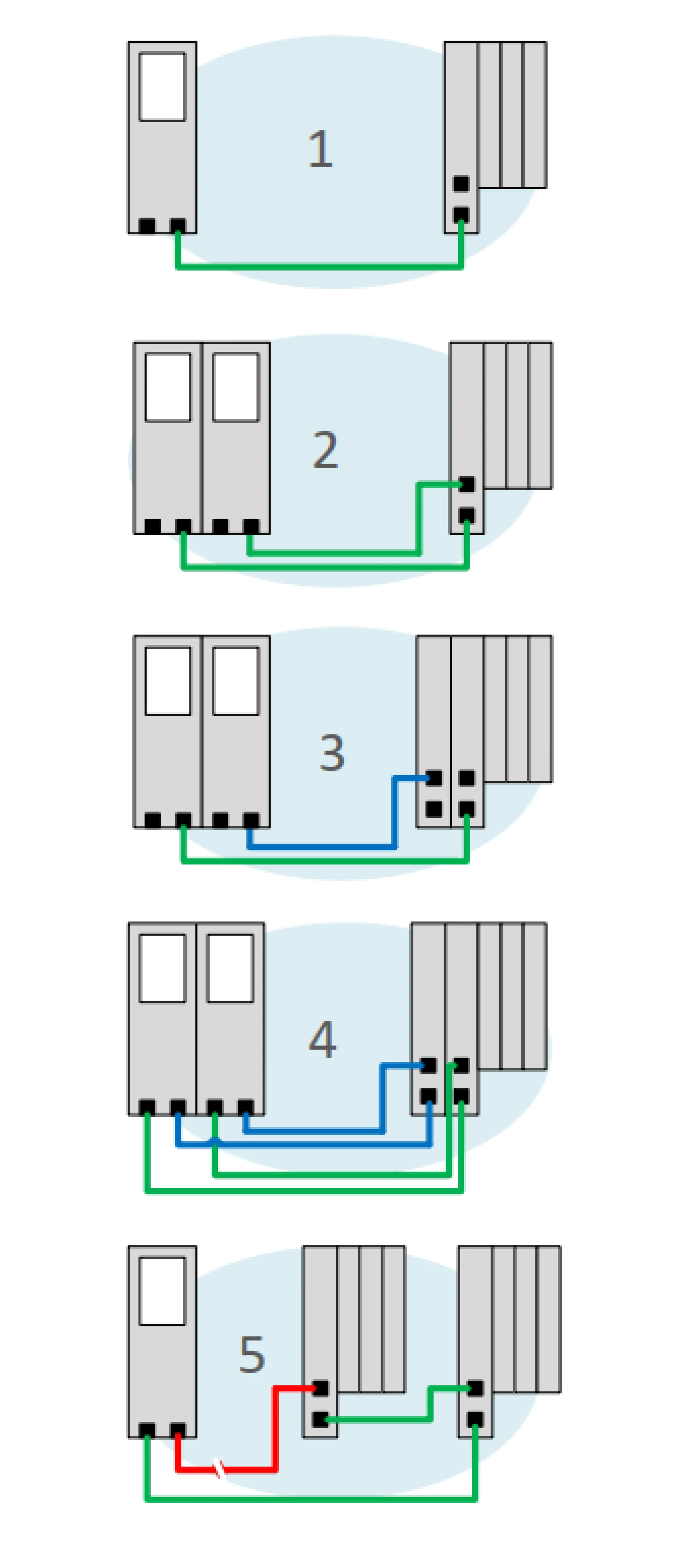
Four System Redundancy Topologies
1. S1 System Redundancy
Here, the IO devices are connected to the controller without any redundancies. An interruption in the communication connection leads to a failure of the components.
2. S2 System Redundancy
This involves controller redundancy in combination with logical redundancy on the component side. These are connected to the controllers in an open ring. If the primary controller fails or communication is interrupted, the secondary controller is automatically activated and all components establish the connection individually. However, if an interface module fails, the component fails completely.
3. R1 System Redundancy
This is a combination of controller and network redundancy. Each component is connected to a controller via two interface modules. Compared to system redundancy S2, the system differs in that it has two separate networks, thus offering protection against a network failure. If an interface module fails, the component is still available. The disadvantage of this solution is the double volume of cables used.
4. R2 System Redundancy
R2 redundancy is a combination of S2 and R1 redundancy. Accordingly, both logical and physical redundancy is provided on the controller and component side. This structure means that a fault can occur at network and controller level without affecting the functionality of the system.
5. Media Redundancy Protocol
In addition to the system redundancies, Profinet supports the media redundancy protocol (MRP), which ensures availability through a ring topology. MRP is a logical redundancy. A ring master blocks one port of the ring and communicates with all IO devices via the other. If the master loses the connection to one or more IO devices due to a wire break or failure of an IO device, the second port is released and communication is re-established via it.
Conclusion
Profinet supports many standardised options for setting up system redundancy. These can also be freely combined to create additional security for critical applications. However, it's important to bear in mind that not all connection options and protocols are available for all control systems and components. This must therefore be clarified before the system topology is defined and the system adapted accordingly.
CTE is currently working on applying Profinet to other control systems with the aim of increasing safety in our customers' high-availability systems.


